Your BMI is a measurement of your body weight based on your height and weight. Although your BMI does not actually “measure” your percentage of body fat, it is a useful tool to estimate a healthy body weight based on your height. Due to its ease of measurement and calculation, it is the most widely used diagnostic indicator to identify a person’s optimal weight depending on his height. Your BMI “number” will inform you if you are underweight, of normal weight, overweight, or obese. However, due to the wide variety of body types, the distribution of muscle and bone mass, etc., it is not appropriate to use this as the only or final indication for diagnosis.
Body Mass Index Formula
The formulas to calculate BMI based on two of the most commonly used unit systems:
- BMI = weight(kg)/height2(m2) (Metric Units)
BMI = 703·weight(lb)/height2(in2) (U.S. Units)
BMI Table for Adults
This is the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended body weight based on BMI values for adults. It is used for both men and women, age 18 or older.
| Category | BMI range – kg/m2 |
| Severely underweight | < 16.5 |
| Underweight | 16.5 – 18.5 |
| Normal | 18.5 – 25 |
| Overweight | 25 – 30 |
| Obese Class I | 30 – 35 |
| Obese Class II | 35 – 40 |
| Obese Class III | > 40 |
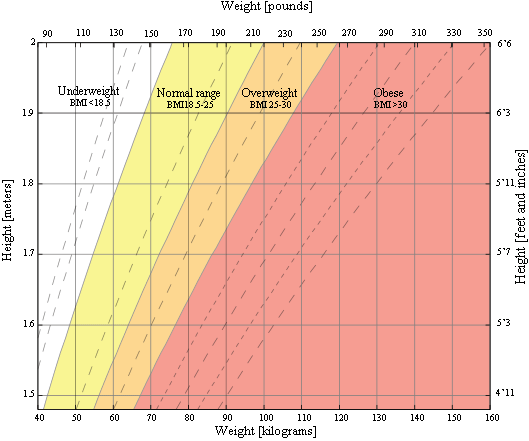
BMI Chart for Adults
This is a graph of BMI categories based on the World Health Organization data. The dashed lines represent subdivisions within a major categorization.
BMI Table for Children and Teens, Age 2-20
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends BMI categorization for children and teens between age 2 and 20.
| Category | Percentile Range |
| Underweight | <5% |
| Healthy weight | 5% – 85% |
| At risk of overweight | 85% – 95% |
| Overweight | >95% |